Baseball Position Generator
A practical tool for Little League coaches to generate fair, rotation-based defensive positions.
2022-05-01
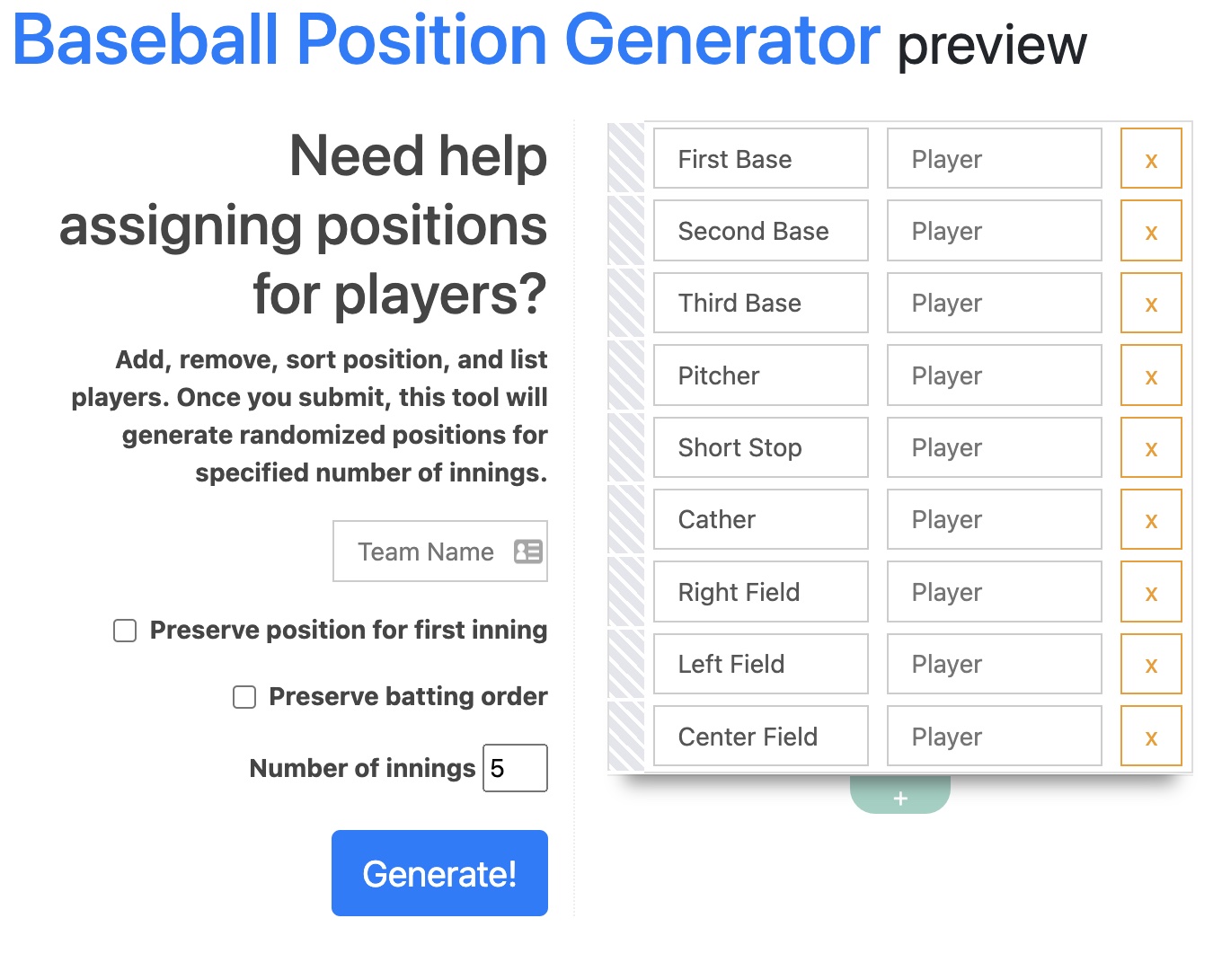
Executive Summary
The Baseball Position Generator is a lightweight, Flask-based web app designed to help Little League and recreational baseball coaches generate fair, rotation-based defensive positions across games and innings.
Unlike competitive or analytics-heavy baseball software, this project focused on practical coaching constraints: fairness, transparency, and ease of use. The tool was built and refined during an actual season and used to support real teams with varying skill levels and participation goals.
This project predates my work with AI-assisted development and reflects a more traditional, domain-driven engineering approach.
1. Problem
Managing defensive positions for a youth baseball team is deceptively difficult.
Coaches must balance:
- Fair playing time across positions
- Player safety and skill development
- Parental expectations
- Limited time during games
- Incomplete attendance from game to game
Manual rotation quickly becomes error-prone, especially over the course of a season. Without structure, some players unintentionally receive less exposure to certain positions, which can lead to frustration and perceived unfairness.
Existing tools tended to focus on advanced statistics or competitive optimization, rather than the everyday realities of recreational coaching.
2. Context and Constraints
This project was developed in the context of Little League and recreational baseball, where:
- Player development and enjoyment matter more than optimization
- Teams change week to week due to attendance
- Coaches often operate under time pressure
- Tools must be simple enough to explain to parents if needed
The solution needed to be:
- Deterministic and explainable
- Flexible to roster changes
- Easy to run without complex setup
3. Approach
I approached the problem as a constraint-satisfaction and rotation problem, not an optimization problem.
Key principles:
- Every player should experience a variety of positions over time
- No single game should overly bias assignment
- The system should be transparent and predictable
The implementation used:
- A Flask web UI deployable to Heroku
- URL parameter-based inputs to pre-populate initial positions and batting orders
- Deterministic logic to assign positions by inning
- Simple output that could be printed or shared digitally
Rather than building a UI-heavy application, I focused on correctness, clarity, and adaptability.
4. Design Decisions
Fairness Over Optimization
The goal was not to maximize competitive advantage, but to ensure fair exposure to positions across the season. This shaped the entire algorithmic approach.
Explainability
Assignments needed to be explainable to players and parents. This ruled out opaque heuristics or complex scoring systems.
Minimal Tooling
Flask and a lightweight web UI kept the barrier to entry low. Coaches could share a link with pre-populated inputs and use the tool without installing software.
Iterative Refinement
The logic evolved during actual use. Edge cases -- such as absences, late arrivals, or limited skill sets -- were handled incrementally based on real feedback.
5. What Shipped
The project delivered:
- A Flask web app deployable to Heroku
- URL parameter-based input to pre-populate initial positions and batting orders
- Support for inning-by-inning rotation
- Deterministic output suitable for printing or sharing
The tool was used in real coaching scenarios and adjusted over time to reflect on-field realities.
6. What This Project Demonstrates
This project highlights several engineering characteristics that remain relevant today:
- Deep understanding of domain-specific constraints
- Willingness to prioritize human factors over technical novelty
- Iterative development informed by real usage
- Bias toward simplicity and explainability
Although this work predates my use of AI-assisted development, it reflects the same core principle that underlies my later projects: good software starts with understanding the people and workflows it serves.
7. Relationship to Later Work
This project represents an earlier phase of my engineering approach -- before AI acceleration -- where iteration speed was constrained primarily by manual implementation.
In later projects such as RallyHub, AI-assisted development changed how fast systems could be built, but not what mattered: clarity of requirements, domain understanding, and human-centered design.
In that sense, this project forms a natural contrast and foundation for my more recent work.
References
- Blog post: https://trail-route-analytics.blogspot.com/2022/05/managingcoaching-little-league-team.html
- Source code: https://github.com/yama-kei/baseball_position_generator